Unleashing the Power of Programmability
We build awesome programmable devices. One AmP chip combines up to 10 power rails, analog, and digital components into a compact 5mm x 5mm package.
Programmable power designed with AI
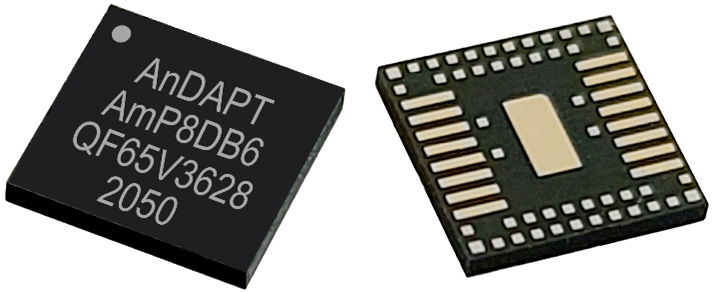
Products
AnDAPT offers power products for popular FPGAs/SoCs like Xilinx, Altera, and Microchip while also offering custom ICs designed based on your requirements.
Benefits
Integrated Functionality
Integrating up to 10+ rails with analog and digital functions.
Advanced Programmability
Program AmP IC within minutes for fast changes or different applications.
Proven Designs
Tested and ready-to-use designs for popular SoCs/FPGAs applications.
Space Saving
More than 17% PCB space saving in comparison to competitor designs.
Easy to Configure
Easy to configure designs allow for a more stress-free building process.

Time-to-Market
Reduced design hours means a faster time-to-market.
Our Partners

Power Partner

Distribution Partner

Distribution Partner

Eco-System Partner

Eco-System Partner

Eco-System Partner

Eco-System Partner

Eco-System Partner

Eco-System Partner

Foundry & Assembly

Foundry & Assembly
One AmP Chip

+
Custom Power Products designed by AnDAPT
+
Power Products available for Xilinx, Altera, Microchip FPGAs
<
We create custom Power Solutions within 24 hours
+
Number of integrated power rails in 1 PMIC
One AmP Chip
+
Custom Power Products designed by AnDAPT
+
Power Products available for Xilinx, Altera, Microchip FPGAs

<
We create custom Power Solutions within 24 hours
+
Number of integrated power rails in 1 PMIC
One AmP Chip
+
Custom Power Products designed by AnDAPT
+
Power Products available for Xilinx, Altera, Microchip FPGAs

<
We create custom Power Solutions within 24 hours
+
Number of integrated power rails in 1 PMIC




